 What to eat during pregnancy to not gain weight, been trying to ...
What to eat during pregnancy to not gain weight, been trying to ...Most women should gain somewhere between 25 and 35 pounds (11.5 to 16 kg) during pregnancy. Most will get 2 to 4 pounds (1 to 2 kg) during the first trimester, and then 1 pound (0.5 kilograms) a week for the remainder of the pregnancy. Total weight gain depends on your situation.
A balanced ,, along with exercise, is the basis for a healthy pregnancy. For most pregnant women, the right amount of calories are:
Most of the weight you gain during pregnancy is not fat, but related to the infant. Here is a breakdown of how 35 pounds (16 kilograms) add up to:
Some women are overweight when they become pregnant. Other women gain weight too quickly during their pregnancy. Either way, a pregnant woman should not go on a diet or trying to lose weight during pregnancy.
It is better to focus on eating the right foods and stay active. If you do not get enough weight during pregnancy, you and your baby may have a problem.
However, you can make changes in your diet to get the nutrients you need without too much weight gain. Talk with your health care provider for assistance with planning a healthy diet
Here are some healthy eating tips to help you start
Healthy choice: ..
Food which should be avoided:
Eat:
Cooking at home:
training:
If you have struggled with your weight in the future then, it may be difficult to accept that it is ok to put on weight now. It is normal to feel anxious as the numbers on the scale edge up.
Keep in mind that you need to gain weight for a healthy pregnancy. Extra pounds will come from after you have your baby. However, if you gain more weight than is recommended, your baby will also be greater. That sometimes can cause problems with delivery. A healthy diet and regular exercise is the best way to ensure a healthy pregnancy and baby.
prenatal care - managing your weight
Bodnar LM, Himes KP. maternal nutrition. In: Resnik R, Lockwood CJ, Moore TR, Greene MF, Copel JA, Silver RM, Eds. Creasy and Resnik's Mother-Fetal Medicine: Principles and Practice. ed 8. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019 :. Chap 12
West EH, Hark L, Catalano PM. Nutrition during pregnancy. In: Gabbe SG, Niebyl JR, Simpson JL, et al, eds. Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancy. ed 7. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2017 :. Chap 7
Updated by: John D. Jacobson, MD, Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Loma Linda University School of Medicine, Loma Linda Fertility Center, Loma Linda, CA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and A.D.A.M. the editorial team.
, For the Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC is an independent audit to verify A.D.A.M. that follows the strict standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. was among the first to achieve this important distinction for health information and services online. Learn more about A.D.A.M. and. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complied with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information.
The information provided should not be used during a medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of a medical condition. A licensed physician should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Call 911 for all medical emergencies. Links to other websites are provided for information only - they do not constitute endorsement of the other sites. Copyright 1997-2020, A.D.A.M., Inc. Duplication for commercial use must be authorized in writing by ADAM Health Solutions.
 Pin on Fit Pregnancy
Pin on Fit Pregnancy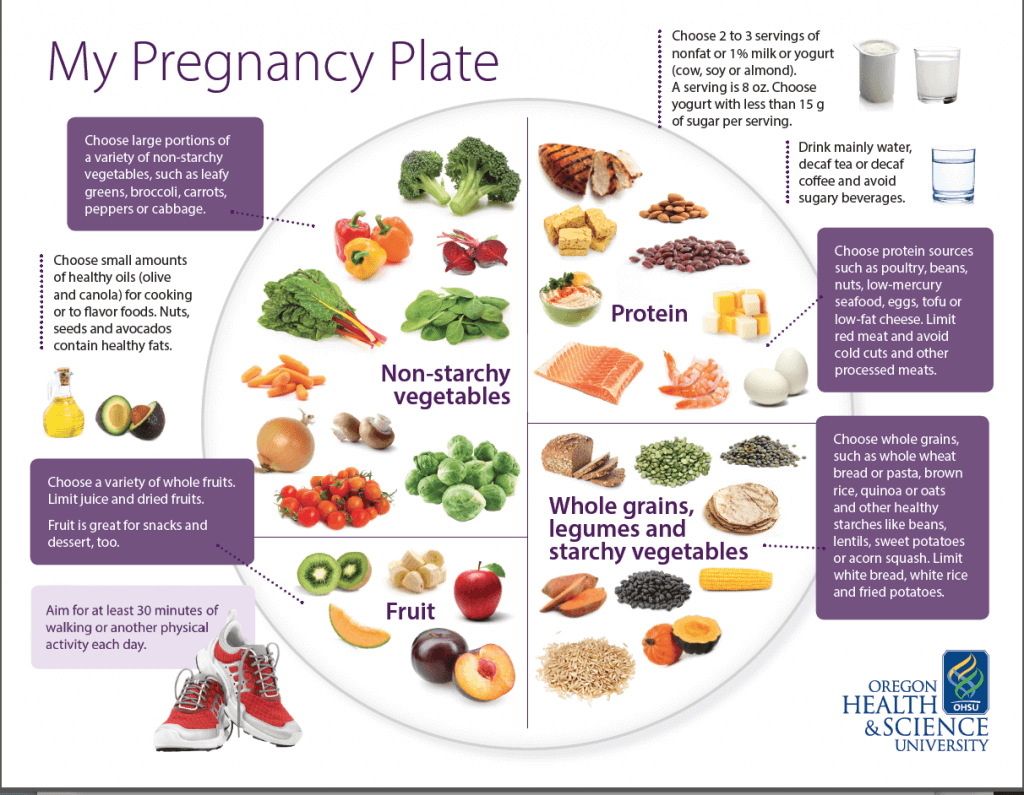 Top 10 foods to include during pregnancy and after! - Calorie Care
Top 10 foods to include during pregnancy and after! - Calorie Care:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/underweight-while-pregnant-4589291_final2-cad7024e794947c4a6097b135c6d57e8.png) What to Know If You Are Underweight While Pregnant
What to Know If You Are Underweight While Pregnant 10 ways to avoid gaining too much pregnancy weight | BabyCenter
10 ways to avoid gaining too much pregnancy weight | BabyCenter Pin on Pregnancy Tips
Pin on Pregnancy Tips How To Lose Weight While Pregnant - 6 Healthy Weight Loss Tips
How To Lose Weight While Pregnant - 6 Healthy Weight Loss Tips 9th Month Pregnancy Diet - Which Foods To Eat And Avoid?
9th Month Pregnancy Diet - Which Foods To Eat And Avoid?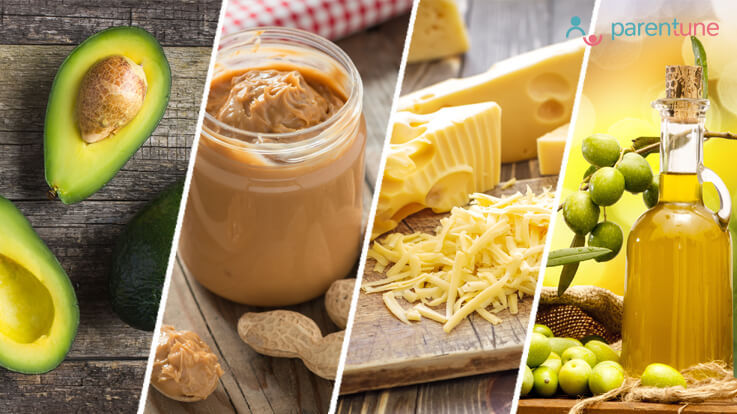 Parentune - 19 Foods to Help Baby Fetal Weight Gain During Pregnancy
Parentune - 19 Foods to Help Baby Fetal Weight Gain During Pregnancy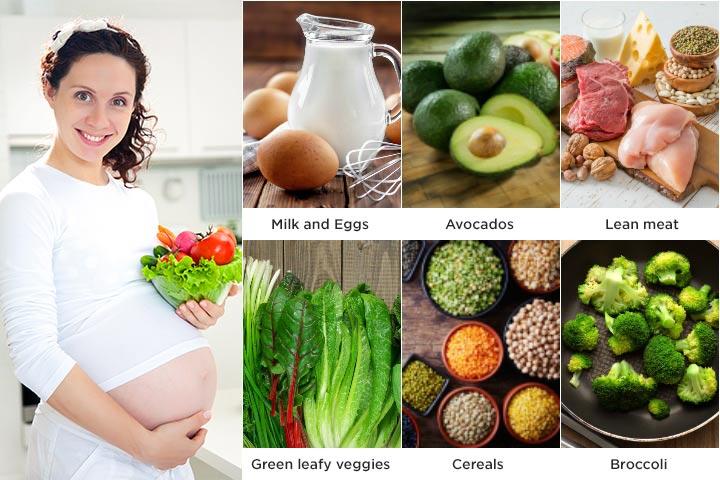 8 Month Pregnancy Diet – Which Foods To Eat And Avoid?
8 Month Pregnancy Diet – Which Foods To Eat And Avoid? Pin on Santi
Pin on Santi Pregnancy and Weight Gain - How Much is Too Little?
Pregnancy and Weight Gain - How Much is Too Little? Weight Gain During Pregnancy
Weight Gain During Pregnancy 7th Month Pregnancy Diet - Which Foods To Eat And Avoid?
7th Month Pregnancy Diet - Which Foods To Eat And Avoid? 3 Ways to Avoid Gaining Baby Weight - wikiHow
3 Ways to Avoid Gaining Baby Weight - wikiHow 7 Secrets to Prevent Excess Weight Gain During Pregnancy | Haute ...
7 Secrets to Prevent Excess Weight Gain During Pregnancy | Haute ... How to Lose Weight While Pregnant: 10 Steps (with Pictures)
How to Lose Weight While Pregnant: 10 Steps (with Pictures) What You Need to Know About Your Pregnancy Diet Chart
What You Need to Know About Your Pregnancy Diet Chart Pregnancy diet: Under-eating | Parenthub
Pregnancy diet: Under-eating | Parenthub Can you lose weight during pregnancy? How to stay safe
Can you lose weight during pregnancy? How to stay safe Second Trimester Diet: Daily Requirements, Cravings, Tips, and More
Second Trimester Diet: Daily Requirements, Cravings, Tips, and More 13 Foods to Eat When You're Pregnant
13 Foods to Eat When You're Pregnant Newcastle Hospitals - Healthy eating
Newcastle Hospitals - Healthy eating Not Gaining Enough Weight During Pregnancy
Not Gaining Enough Weight During Pregnancy Eat Well, Lose Weight, While Breastfeeding: The Complete Nutrition ...
Eat Well, Lose Weight, While Breastfeeding: The Complete Nutrition ... How to Lose Weight during Pregnancy
How to Lose Weight during Pregnancy Power Snacks You Can Eat Without Gaining Weight
Power Snacks You Can Eat Without Gaining Weight Pregnancy diet: What to eat and what to avoid
Pregnancy diet: What to eat and what to avoid Eating nutrisystem while pregnant
Eating nutrisystem while pregnant The Reason Why You Can't Lose Weight While Breastfeeding
The Reason Why You Can't Lose Weight While Breastfeeding How To Conceive A Boy
How To Conceive A Boy How to Eat to Lose Weight: The Secret to Turning Your Body into a ...
How to Eat to Lose Weight: The Secret to Turning Your Body into a ... 14 foods you can eat as much of as you want and not gain weight ...
14 foods you can eat as much of as you want and not gain weight ... The Truth About Pregnancy Weight Gain | Mama Natural
The Truth About Pregnancy Weight Gain | Mama Natural The best time to eat breakfast, lunch and dinner if you want to ...
The best time to eat breakfast, lunch and dinner if you want to ... Overweight and pregnant: How to manage weight gain during ...
Overweight and pregnant: How to manage weight gain during ... Parentune - How to Increase Baby Weight in 5th, 6th and 7th months ...
Parentune - How to Increase Baby Weight in 5th, 6th and 7th months ... 7 Secrets to Prevent Excess Weight Gain During Pregnancy | Haute ...
7 Secrets to Prevent Excess Weight Gain During Pregnancy | Haute ... How to Lose Weight While Pregnant: 10 Steps (with Pictures)
How to Lose Weight While Pregnant: 10 Steps (with Pictures) Healthy Weight Gain During Pregnancy | Ask Dr Sears
Healthy Weight Gain During Pregnancy | Ask Dr Sears How Much Weight Should You Gain During Pregnancy? Episode 281
How Much Weight Should You Gain During Pregnancy? Episode 281 It's healthier to lose weight before you get pregnant -
It's healthier to lose weight before you get pregnant -/avocado-57012ace5f9b58619531fe7f.jpg) How Children Can Gain Weight Healthily
How Children Can Gain Weight Healthily 6 Foods That Could Make You Gain Weight | Health.com
6 Foods That Could Make You Gain Weight | Health.com Pregnancy Weight Gain Calculator - Recommended Weight Gain By Week ...
Pregnancy Weight Gain Calculator - Recommended Weight Gain By Week ... Obese Pregnancy: Weight Loss Tips
Obese Pregnancy: Weight Loss Tips 15 Foods You Can Eat a Lot of and Still Not Gain Weight
15 Foods You Can Eat a Lot of and Still Not Gain Weight Weight Gain During Pregnancy, By Trimester | Healthy Families BC
Weight Gain During Pregnancy, By Trimester | Healthy Families BC Healthy Weight during Pregnancy
Healthy Weight during Pregnancy Pregnancy Weight Gain: Most Women Don't Lose Weight After Birth ...
Pregnancy Weight Gain: Most Women Don't Lose Weight After Birth ... How Many Calories Should You Eat to Lose Weight? | SELF
How Many Calories Should You Eat to Lose Weight? | SELF Weight-Gain Shockers: Stress, Medications, and More
Weight-Gain Shockers: Stress, Medications, and More Pregnancy Weight Gain - The American Pregnancy Association
Pregnancy Weight Gain - The American Pregnancy Association How to Avoid Weight Gain During Pregnancy | POPSUGAR Fitness
How to Avoid Weight Gain During Pregnancy | POPSUGAR Fitness April's issue by The Fitness and Lifestyle Magazine - issuu
April's issue by The Fitness and Lifestyle Magazine - issuu Why Am I Losing Weight While Pregnant? | Parents
Why Am I Losing Weight While Pregnant? | Parents 14 foods you can eat as much as you want and not gain weight
14 foods you can eat as much as you want and not gain weight Not gaining weight during pregnancy. What to do? — MediMetry ...
Not gaining weight during pregnancy. What to do? — MediMetry ...
Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar