 Food Packages - Johnson County Community Health Services
Food Packages - Johnson County Community Health ServicesHow it .gov government website official.Federal always use .gov or domain Mil. Before sharing sensitive information online, make sure you are deploying or Mil sites by checking your browser's address (or "location") bar.
This site is also protected by SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) certificate that was signed by the US government. Https: // means all data transmitted is encrypted - in other words, information or browsing history you provide is transmitted safely
Pregnant, postpartum and breastfeeding women, infants, and children up to age 5 who qualify. They must meet income guidelines, state residency requirements, and the individually determined to be at "nutritional risk" by health professionals.
To qualify on the basis of income, gross income applicants (ie before taxes withheld) must fall at or below 185 percent of the US Poverty Income Guidelines.
Every year
Monthly
Weekly
While most countries use the guideline maximum, the state may set the standard a lower income limit. A person or certain family members who participate in programs other benefits such as Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program, Medicaid, or Temporary Assistance for Needy Families automatically meet the income eligibility requirements.
The two main types of nutritional risk are recognized for WIC eligibility:
nutritional risk determined by a healthcare professional such as a doctor, dietician or nurse, and is based on federal guidelines. health screening is free to program applicants.
Beginning April 1, 1999, state agencies using WIC nutrition risk criteria from a list established for use in the WIC Program. WIC nutrition risk criteria developed by FNS in conjunction with state and local WIC agency experts. WIC state agencies are not required to use all of the nutritional risk criteria in the new list. FNS will update the list of criteria, as necessary, when new scientific evidence showed, after a review by FNS and other health and nutrition experts, that the condition can be improved by providing WIC program benefits and services.
During the fiscal year (FY) 2018, the number of women, infants, and children who receive WIC benefits each month reached approximately 6.87 million. For the first 5 months of FY 2019, the state reported a monthly average participation of over 6.4 million participants per month. In 1974, the first year permanently WIC officially, 88,000 people participated. In 1980, participation was at 1.9 million; by 1985, 3.1 million; in 1990, 4.5 million; and in 2000, 7.2 million. the average monthly participation for FY 2017 is approximately 7.3 million.
Children always be the largest category of WIC participants. Of the 6.87 million people who receive WIC benefits each month in fiscal year 2018, approximately 3.52 million children, 1.71 million still in its infancy, and 1.63 million were women.
In most state agencies WIC, participants of WIC receive checks or vouchers for certain food purchases each month designed to supplement their diet with specific nutrients that the target population of this WIC benefits. In addition, some state-issued electronic benefit cards to participants instead of paper checks or vouchers. The use of electronic cards is growing and all state institutions WIC WIC necessary to carry out electronic benefit transfer (EBT) in the entire state by October 1, 2020. Some WIC state agencies distribute food through the warehouse or deliver food to the homes of participants. Different food packages are provided for different categories of participants.
WIC foods including infant cereal, iron-fortified adult cereal, vitamin C-rich fruit or vegetable juice, eggs, milk, cheese, peanut butter, dried and canned beans / peas, and canned fish. soy-based beverages, tofu, fruits and vegetables, baby food, whole wheat bread and other wheat selection of recently added to better meet the nutritional needs of WIC participants.
WIC recognizes and promotes breastfeeding as the optimal source of nutrition for infants. For women who do not fully breastfeeding, WIC provides infant formula iron fortified. special infant formula and medical foods may be given when prescribed by a doctor for specific medical conditions.
If WIC can not serve all eligible people who apply for benefits, so the priority system has been set to fill the openings Program. Afterinstitutions WIC local has achieved the load maximum cases, vacancies are generally filled the order of priority as follows:
Mothers participating in WIC are encouraged to breastfeed their babies if possible, but the state agency WIC provides infant formula for mothers who choose to use These feeding methods. WIC state agencies are required by law to have a baby offer competitive rebate formula contract with manufacturers of infant formula. This means WIC state agencies agreed to provide one brand of formula and reward manufacturers provide a rebate for any state agency cans of infant formula purchased by WIC participants. Brand of formula provided by WIC varies by state agencies depends on the company has a rebate contract in certain circumstances.
By negotiating rebates with manufacturers of infant formula, the country can serve more people. For FY 2017, the savings rebate was $ 1.74 billion, supporting an average of 1.55 million participants each month, or 21.25 percent of the caseload of the average monthly estimated.
, founded in 1992, provides additional coupons for WIC participants that they can be used to buy fresh fruits and vegetables at participating farmers markets. FMNP funded through the congressionally mandated set-aside in WIC appropriation. The program has two objectives: To provide fresh, nutritious, ready, fruits and vegetables are locally grown, from the farmers market to the participants of WIC nutrition risk; and to expand consumer awareness and use of farmers markets.
A 15 November each year, each implementing or participating state agencies must submit to FNS Regional Office for the approval of the State Plan for the next year as a prerequisite for receiving funds. FMNP the guidance of the State Plan is also available from the Regional Office of FNS.
An administrative agency may FMNP state agriculture department, health department, or other institutions approved by the executive heads of state or Indian Tribal organization.
Contact the USDA Food and Nutrition Service Public Information Staff at 703-305-2286, or by mail at 3101 Park Center Drive, Room 819, Alexandria, Virginia 22302.
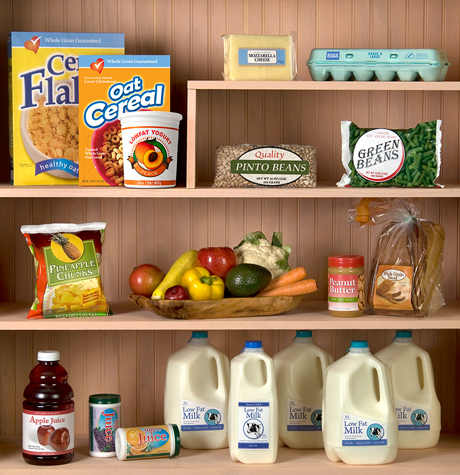 Food Packages | Texas WIC
Food Packages | Texas WIC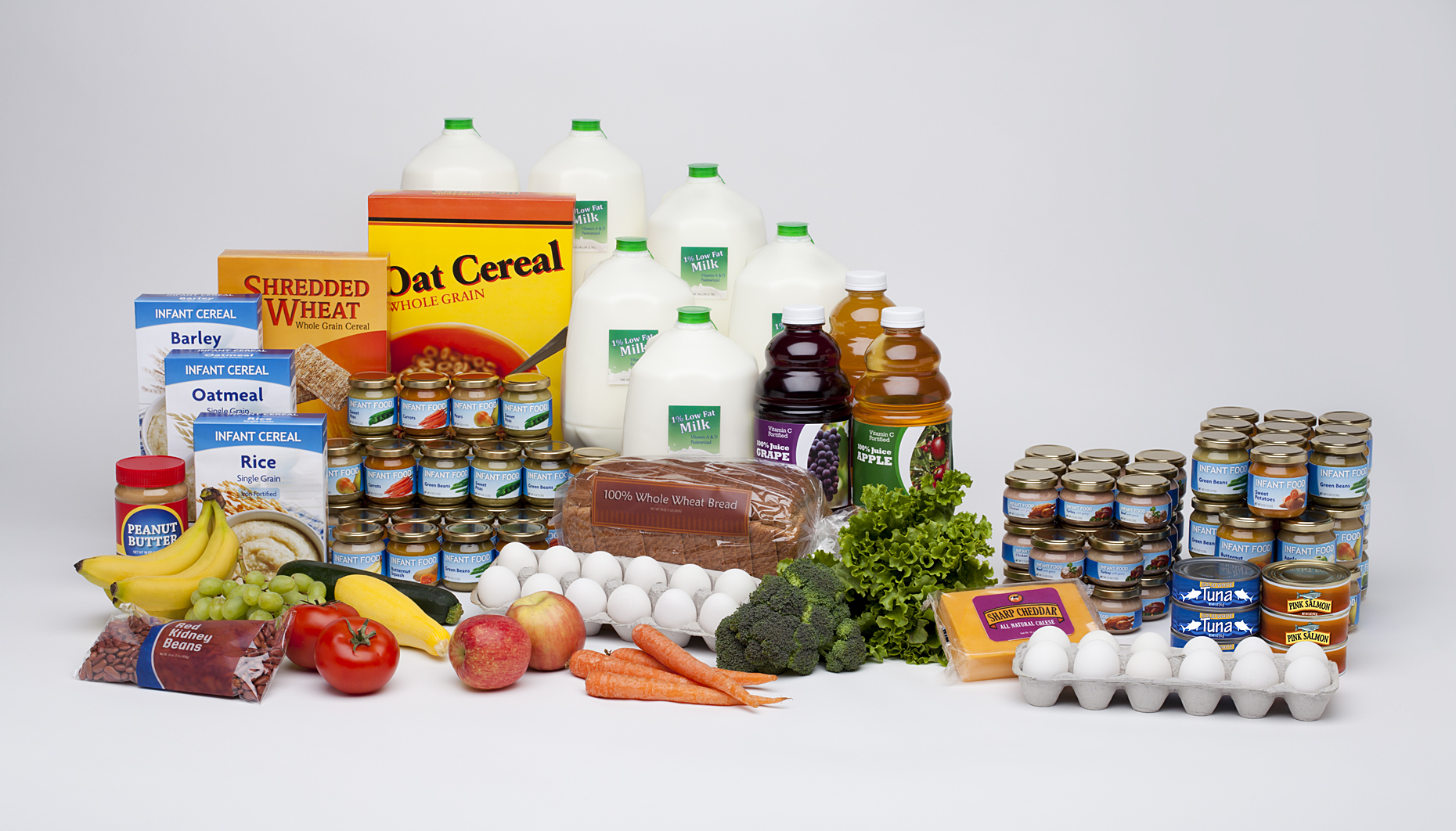 What's in Your WIC Food Package | WIC Breastfeeding
What's in Your WIC Food Package | WIC Breastfeeding Guideline for Choosing Food Packages - Nevada WIC
Guideline for Choosing Food Packages - Nevada WIC Guideline for Choosing Food Packages - Nevada WIC
Guideline for Choosing Food Packages - Nevada WIC Texas WIC Food List
Texas WIC Food List Some WIC Food Packages! Which would you choose? #WIC #Nutrition ...
Some WIC Food Packages! Which would you choose? #WIC #Nutrition ... View the Tennessee WIC Food List
View the Tennessee WIC Food List View the Florida WIC Food List
View the Florida WIC Food List Food Packages | Texas WIC
Food Packages | Texas WIC Texas WIC Food List
Texas WIC Food List Guideline for Choosing Food Packages - Nevada WIC
Guideline for Choosing Food Packages - Nevada WIC Women, Infants, and Children (WIC) - CUPHD
Women, Infants, and Children (WIC) - CUPHD Kentucky WIC Food List
Kentucky WIC Food List wic baby food chart - Vatan.vtngcf.org
wic baby food chart - Vatan.vtngcf.org Food Benefits | San Diego WIC
Food Benefits | San Diego WIC Food Packages | Texas WIC
Food Packages | Texas WIC Guideline for Choosing Food Packages - Nevada WIC
Guideline for Choosing Food Packages - Nevada WIC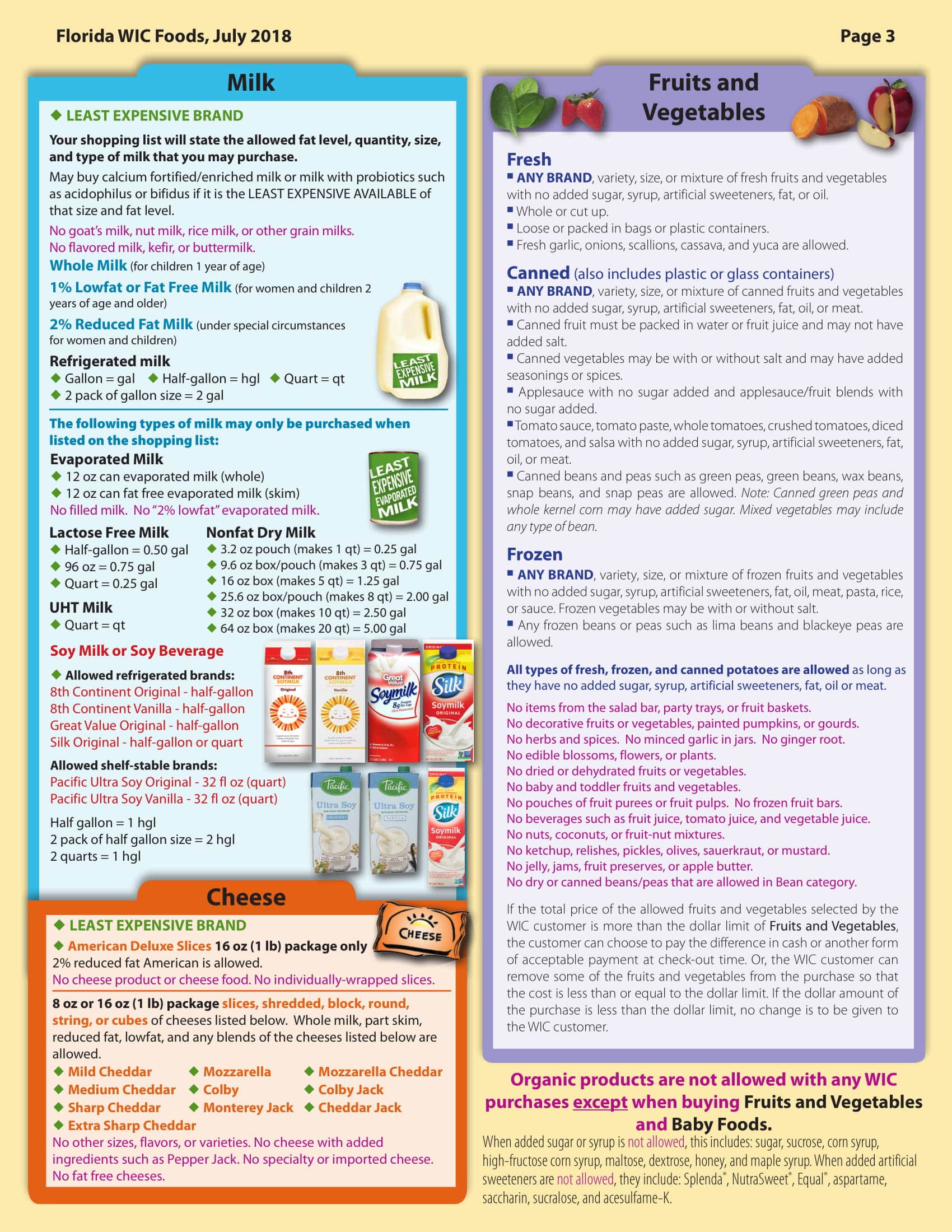 View the Florida WIC Food List
View the Florida WIC Food List Tennessee WIC Food List
Tennessee WIC Food List MD WIC
MD WIC WIC Approved Foods - Oklahoma State Department of Health
WIC Approved Foods - Oklahoma State Department of Health Food Packages | Texas WIC
Food Packages | Texas WIC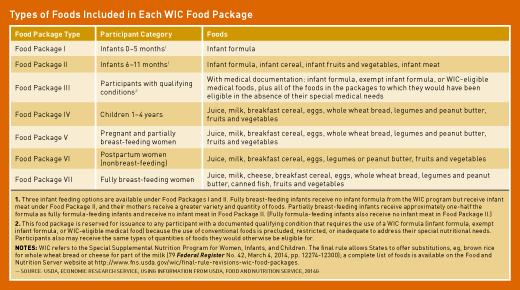 An Update on WIC - Today's Dietitian Magazine
An Update on WIC - Today's Dietitian Magazine Home - WIC
Home - WIC Oregon Health Authority : WIC Food List : Oregon WIC Program ...
Oregon Health Authority : WIC Food List : Oregon WIC Program ... Food Packages and Infant Formula – WIC Participants
Food Packages and Infant Formula – WIC Participants Florida WIC Food List
Florida WIC Food List WIC | Summit County Public Health
WIC | Summit County Public Health View the Texas WIC Food List
View the Texas WIC Food List WIC HomePage | Department of Health | State of Louisiana
WIC HomePage | Department of Health | State of Louisiana For Participants
For Participants The federal program to feed pregnant women and children, WIC, is a ...
The federal program to feed pregnant women and children, WIC, is a ... Food Packages and Infant Formula – WIC Participants
Food Packages and Infant Formula – WIC Participants Women, Infants & Children (WIC)
Women, Infants & Children (WIC) Foods you can buy with Indiana WIC benefits
Foods you can buy with Indiana WIC benefits New WIC food list announced
New WIC food list announced 31 Best WIC - English images | Food, This or that questions, Food ...
31 Best WIC - English images | Food, This or that questions, Food ... View the Hawaii WIC Food List
View the Hawaii WIC Food List WIC Foods
WIC Foods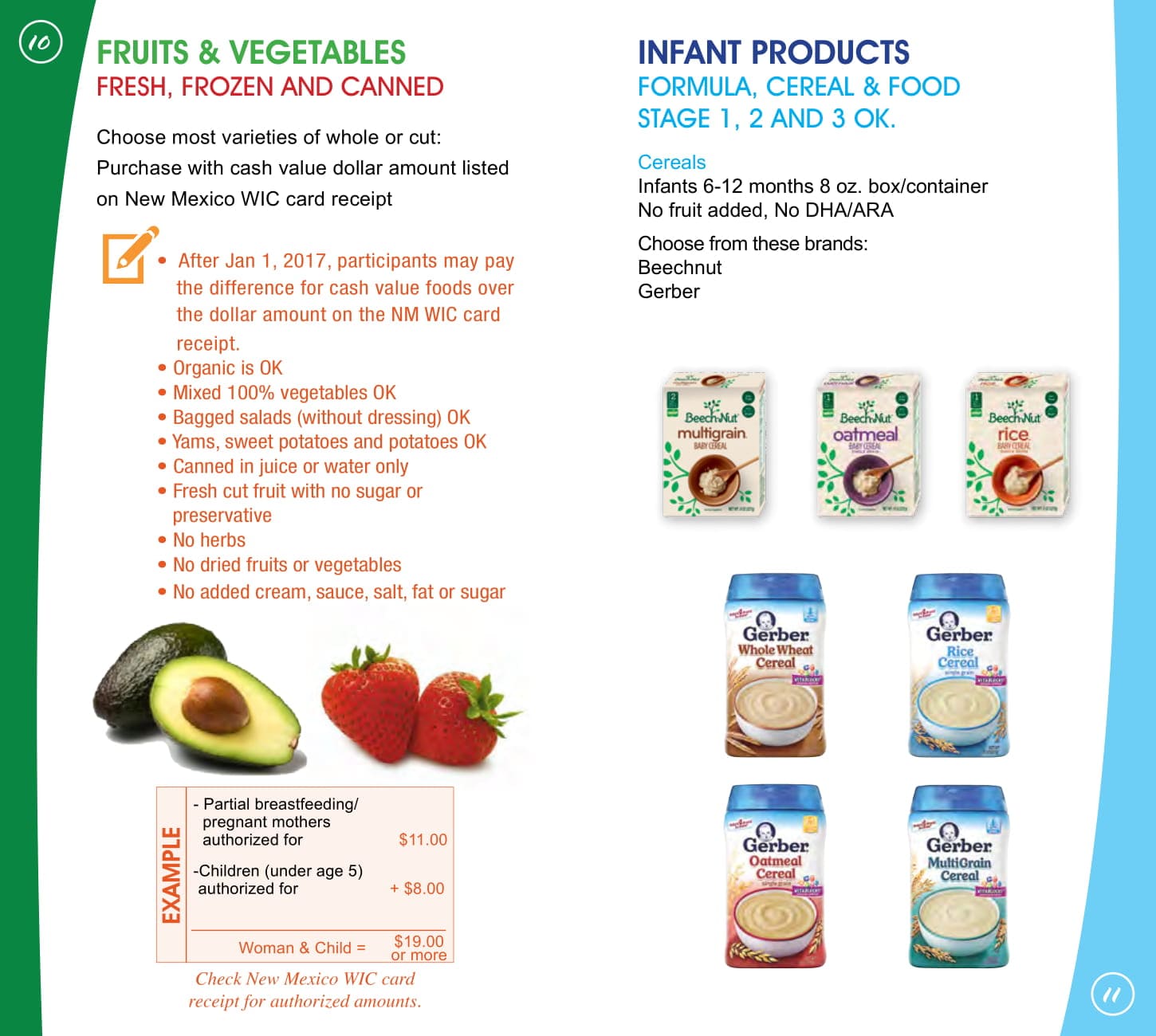 Foods you can buy with New Mexico WIC benefits
Foods you can buy with New Mexico WIC benefits Texas WIC Food List
Texas WIC Food List Shopping with WIC | Vermont Department of Health
Shopping with WIC | Vermont Department of Health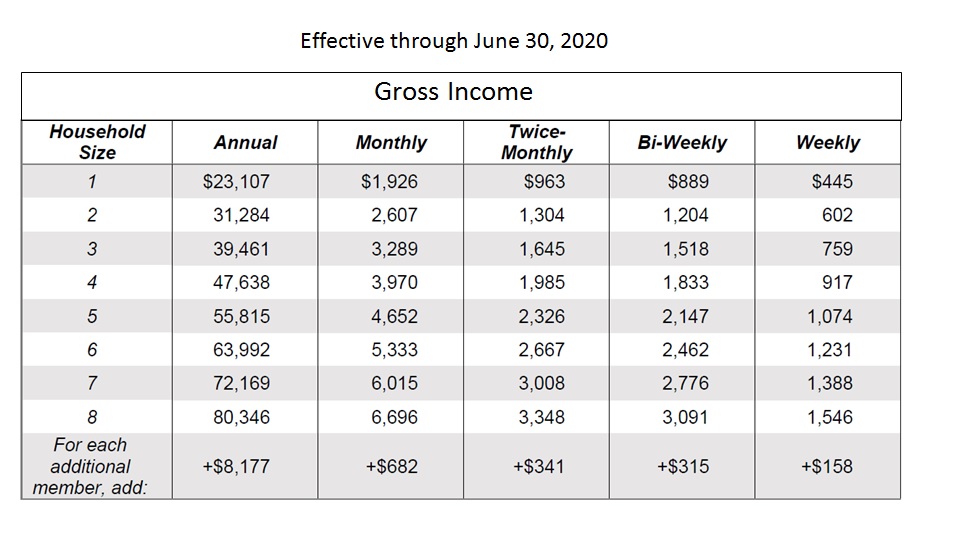 WIC | Delaware Opportunities Inc.
WIC | Delaware Opportunities Inc. About WIC | Pettis County Health Center
About WIC | Pettis County Health Center My life on WIC - Confessions
My life on WIC - Confessions Department of Health | WIC
Department of Health | WIC Archive - California Agriculture
Archive - California Agriculture WIC Approved Foods List | Georgia Department of Public Health
WIC Approved Foods List | Georgia Department of Public Health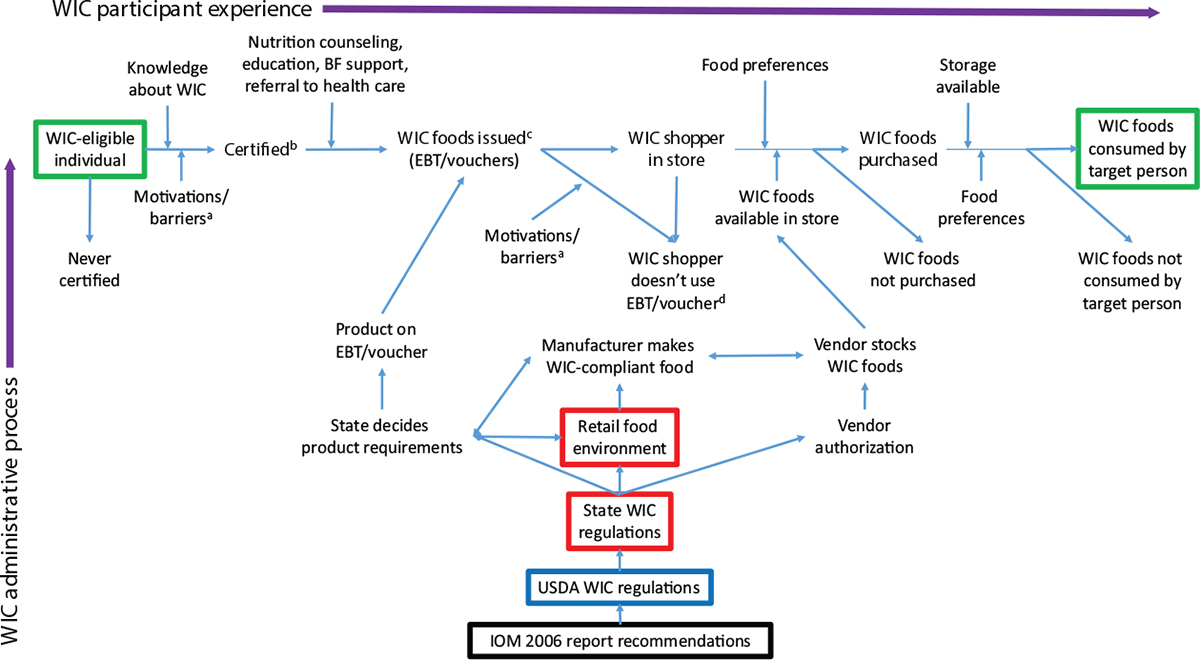 2 The WIC Participant Experience | Review of WIC Food Packages ...
2 The WIC Participant Experience | Review of WIC Food Packages ... Plant-Based on WIC - Plant Based on a Budget
Plant-Based on WIC - Plant Based on a Budget WIC Participant Handbook for Women, Infants, and Children
WIC Participant Handbook for Women, Infants, and Children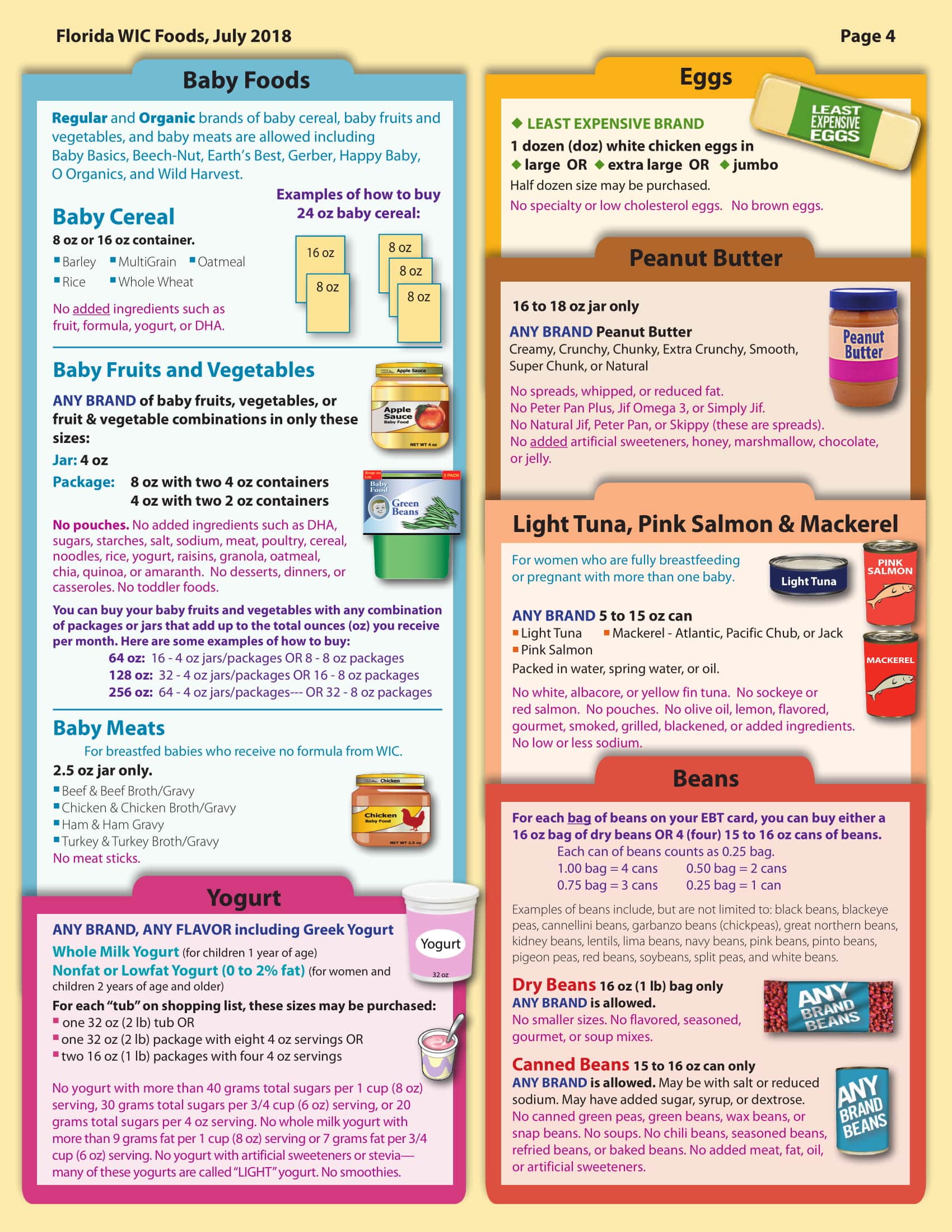 View the Florida WIC Food List
View the Florida WIC Food List Food Shopping Guide - Wyoming Department of Health
Food Shopping Guide - Wyoming Department of Health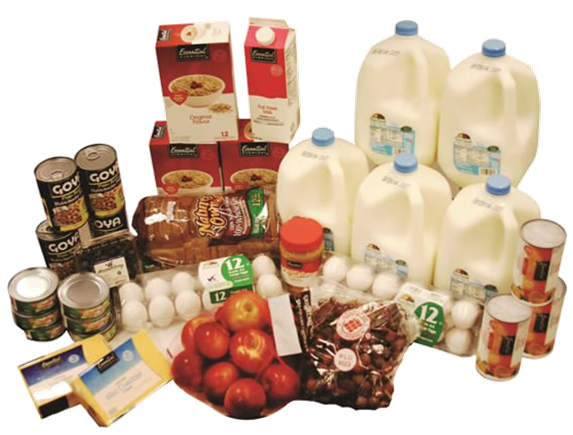 Food Packages and Infant Formula – WIC Participants
Food Packages and Infant Formula – WIC Participants Tennessee WIC Food List
Tennessee WIC Food List
Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar